FSSC22000 STANDARD: NEW IN VERSION 6
April 15, 2023
THE BASIC PRINCIPLES INCORPORATED IN THE ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION MANAGEMENT SYSTEM STANDARDS
May 3, 2023The ISO 9000 series of standards is actually a set of international documents related to quality assurance, adopted by the ISO organization in 1987, to be amended almost every five years. Their objective is to help organizations in establishing and properly implementing a quality management system.
These standards provide requirements and guidelines for designing and evaluating management systems. The ISO 9000 series of standards does not refer to any product or service, nor does it contain requirements that must be met by a product or service, so that a product or service cannot be controlled against the standard. In Serbia, this series of standards was published by the Institute for Standardization of Serbia and the standards bear the mark “SRPS” before the name of the standard. The series consists of standards:
1. ISO 9000: 2015 – Quality management system – basics and vocabulary (SRPS ISO 9000: 2015)
2. ISO 9001: 2015 – Quality management system – requirements (SRPS ISO 9001: 2015)
3.ISO 9004: 2018 – Recommendations for achieving sustainable success of the organization – approach through quality management (SRPS ISO 9004: 2018)
The ISO 9000 : 2015 standard contains the vocabulary and concepts on which this series of standards is based. The document is of a descriptive nature, it does not contain any requirements, but it contains a description of the eight principles of quality management.
The ISO 9001 : 2015 standard contains requirements for a quality management system and the organization is checked and certified against this standard.
The ISO 9004 : 2018 standard provides instructions to organizations for achieving sustainable development through a quality management approach. Organizations achieve sustainable development by meeting the needs and expectations of their users and other interested parties over a long period of time. ISO 9004 requires the organization to achieve efficiency and effectiveness in everything it does, which makes this standard more dedicated to the quality management system compared to ISO 9001, which requires the organization to be effective in everything it does.
(Effectiveness according to ISO 9000: measure of realization of planned activities and planned results.
Efficiency according to ISO 9000: ratio of achieved results and used resources)
Features of the ISO 9000 series standard:
• general in nature and applicable in all types of organizations
• they do not set criteria for products and services – they are not of a technical nature
• do not replace but supplement the specified requirements for the product or service
• do not impose a uniform structure of the quality management system
• are based on a process approach
• are based on the PDCA methodology
• voluntary implementation of standards
The ISO 9001 standard belongs to the series of ISO 9000 standards and is an international standard that contains requirements for the quality management system (QMS) in organizations. This is the only standard in the ISO 9000 series that assesses the conformity of a QMS.
The ISO 9001 standard is based on a preventive approach to quality (an approach based on risk assessment), which covers a wide range of requirements related to suppliers, management commitment to quality, customer focus, resource quality, employee competencies, quality planning, product development, reviews, etc.
ISO 9001 does not define the requirements for the products and services that the company uses, but for the quality management system, the application of which will demonstrate that the company’s products meet the needs of the users and that it operates in accordance with the current legislation.
Basic approaches incorporated in the quality management system standard
This international standard is based on the principles of quality management described by the ISO 9000 standard and the process approach during the implementation, application and improvement of the quality management system.
Process approach
The organization, like other systems, has a certain structure, i.e. it consists of a number of subsystems.
A subsystem of an organization is a set of mutually related processes.
A process represents any activity or set of activities that receives input elements and transforms them into output elements.
Since the organizational system is a complex system, which is composed of a large number of interrelated processes, in order for the organization to function, the interconnections between these processes must be identified.
According to ISO 9001:2015 (0.3.1.): Defining and managing processes, as well as their interaction so that the expected results are achieved in accordance with the quality policy and strategic direction of the organization, is a process approach.
According to ISO 9000 (point 2.4), the aim of this series of international standards is to encourage the adoption of a process approach in the management of the organization.
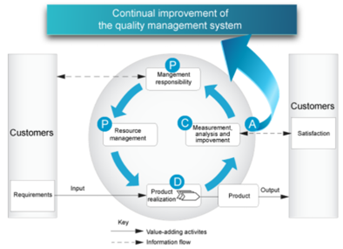
The image shows the quality management system based on the process approach. In the picture it can be seen that the stakeholders have a significant role in securing the input elements of the organization. Monitoring the satisfaction of interested parties requires the evaluation of information, which refers to the observations of interested parties about the extent to which their needs and expectations have been met. Model in picture no. it does not show processes at the level of detail.
The application of the process approach enables the understanding and fulfillment of requirements, consideration of the process in terms of added value, constant improvement, effective performance of the process.
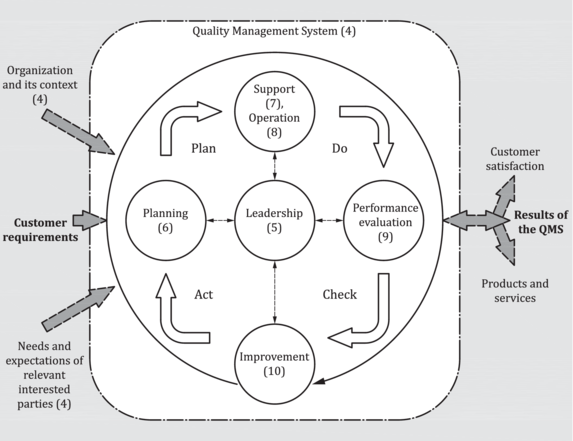
PDCA cycle *
According to ISO 9001:2015 (point 0.3.2), the PDCA cycle (“plan-do-check-act”) can be applied to all processes and to the management system as a whole. The cycle can be described as follows:
Plan: establishing the objectives of the system and its processes, as well as the resources needed to obtain the result in accordance with the requirements of the users and the policy of the organization
Do: implement what is planned
Check: monitor and measure processes, products and services against policy, objectives and product requirements and then report on the results
Act : take action to improve process performance
* The PDCA cycle (Plan-Do-Check-Act) was defined by Walter Shewart, who is considered the originator of modern quality control and the founder of the scientific approach to solving quality-related problems. Edwards Deming is responsible for the wide application of the PDCA cycle, so in practice the PDCA cycle is generally called the Deming cycle. This cycle is associated with solving problems in many areas, not only in the area of quality. The approach consists of four logical steps:
• Plan (Plan): defining the basic elements that need to be achieved
• Do (Do): In relation to the defined elements, it is necessary to start implementation
• Check: evaluation of the achieved results in relation to the planned values
• Act: research into the causes of non-fulfillment of planned settings
Risk-based thinking
The basis for achieving an effective quality management system is risk-based thinking. Risk is a measure of uncertainty and as such can bring positive or negative effects. Positive deviations that occur under the influence of risk lead to opportunities, although it is not necessary that all positive effects will lead to opportunities. Risk-based thinking helps to implement preventive measures, thereby eliminating potential non-conformities, analyzing all non-conformities that may occur and taking actions to prevent their recurrence.
The concept of preventive measures is introduced using risk-based thinking. The ISO 9001:2015 standard requires an organization to plan and establish steps to identify risks and opportunities.
This enabled the establishment of criteria for achieving the effectiveness of the quality management system, achieving improvements and preventing negative effects.
Opportunities may arise as a result of a situation favorable for achieving the intended result. Actions to define opportunities may also include considerations of associated risks.
Risk-based thinking as a concept also exists in the previous version of the ISO 9001 standard (ISO 9001:2008) through the requirements for planning, reviewing and improving. However, in the new version, ISO 9001:2015, the organization is required to understand its context and identify risks as a basis for planning.
IF YOU NEED IMPLEMENTATION, TRAINING, INTERNAL AUDITS, CONSULTATIONS REGARDING QUALITY MANAGEMENT STANDARDS, CONTACT OUR AGENCY!!!!




