THE BASIC PRINCIPLES INCORPORATED IN THE ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION MANAGEMENT SYSTEM STANDARDS
May 3, 2023
FOOD SAFETY CULTURE – NEW TRENDS
June 8, 2023Although that version 8 were expected in January 2023, due to the GFSI suspension, the release was postponed until April: audits according to version 8 are possible from October 1, 2023, while they are mandatory from January 1, 2024.
What are the changes that version 8 brings us? According to IFS, the most significant changes and improvements relate to:
1) The standard is aligned with Codex Alimentarius and the requirements of ISO 22003-2 (a technical specification that provides requirements for certification bodies that conduct audits and certifications) and GFSI benchmarking (GFSI Reference Requirements were created and motivated by the need to harmonize food safety standards throughout the global chain supplies);
2) The B-score is reclassified as a deviation, so that companies can define corrections and corrective actions to continuously improve their performance
3) Introduction of “star status“, as a way to emphasize that the audit was unannounced. This status is visible in the IFS database, where the company’s partners can see the status, thereby highlighting and highlighting the company;
4) Reduction of administrative requirements;
5) Checklist changes: food defense is now part of chapter 4.
6) Companies must define goals for each of the four dimensions of food safety culture.

SCORING SYSTEM
We would say that we are going back to the old one regarding deviation B, but not completely:
For KO requirements, the scoring system now looks like this:
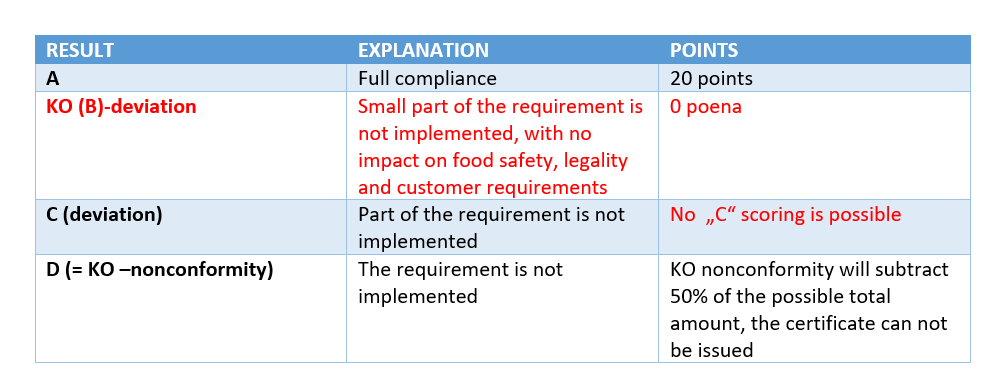
While the assessment of non-KO requests looks like this:
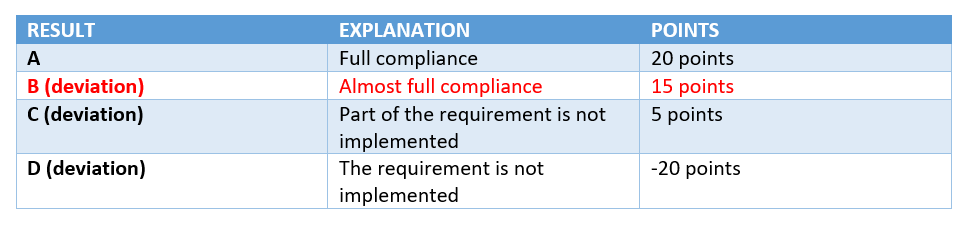
WHAT’S NEW IN THE REQUIREMENTS OF THE STANDARD?
We will list some of the news regarding the requirements of the standard:
- Sustainability has been restored as one of the mandatory positions of the corporate policy (present in version 6.1 but not in version 7);
- 4 dimensions of food safety culture:
• Communication regarding food safety policy and responsibilities
• Trainings
• Employee feedback on food safety issues
• Performance measurement
- Management review and site inspections must be carried out at least once every 12 months, but no more than 15 months
- Chapter 2 traditionally follows HACCP steps and principles, but when identifying the intended use of the product, the identification of consumers is now emphasized; Validation of HACCP plans is required after any modifications that may affect product safety;
- In chapter 3 related to human resources, we have minor changes/additions, such as that personal hygiene rules must include any kind of cigarettes, false nails and eyelashes, covering injuries with waterproof colored plasters, mandatory trainings related to the topic of food fraud- a;
- Chapter 4 brings us a change related to KO request number 4, which until now referred to recipes/formulas. In version 8, this KO requirement is part of the sub-chapter “contracts with customers” and refers to compliance with customer contracts concerning:
• Recipe (including characteristics of raw materials)
• Processes
• Technological requirements
• Test and monitoring plans
• Packaging
• Bookmarks
- Requests for products that have a claim on the labels
- the purchase procedure must provide for procurement in emergency situations
- mandatory verification of labels and documentation of the verification, at least at the beginning and end of production, as well as when changing the product;
- In the cleaning and disinfection plans, we are now obliged to specify the time interval of the planned operations, as well as the CIP cleaning criteria;
- During maintenance, it is mandatory to include all production and storage rooms in preventive maintenance plans, but also to ensure the safety, legality and authenticity of products during and after maintenance;
- Chapter 6-food defense now becomes part of chapter 4, more precisely it comes on 4.21., so the standard now consists of 5 chapters;
- Complaints management must include analysis and time intervals for actions: for complaints from users but also all written notifications from state and control authorities
- The change also occurs in KO request number 9, which now includes recall, withdrawal, incidents and potential emergency situations that may affect the safety, quality, authenticity and legality of the product, so it is necessary to clearly define the procedure (definition of responsibility, training of responsible persons, decision-making process);
- The management of corrective actions is in version 8 the management of deviations, non-conformities, corrections and corrective actions, where the standard requires the user to close non-conformities in a way to prevent their recurrence, which requires an analysis of the causes of non-conformities at least for deviations related to quality, legality, safety, the authenticity of the product but also the deviations that have been repeated.
IF YOU WANT TO FAMILIARIZE WITH THE REQUIREMENTS OF THE IFS FOOD STANDARD VERSION 8, YOU CAN CONTACT US AND PROVIDE YOUR EMPLOYEES WITH PRE-TIME TRAINING!!!




