IFS HPC STANDARD
June 20, 2024
COMPLAINT MANAGEMENT
August 4, 2024To ensure that products and services meet specified requirements and possess certain characteristics in terms of quality, reliability, safety, efficiency, customers resort to evaluating their compliance.
“The process of demonstrating that these characteristics meet the requirements of standards, regulations, and other specifications is called conformity assessment.” Conformity assessment is beneficial both for consumers, who gain confidence in products and services, and for manufacturers and service providers who receive confirmation that their products and services meet user requirements and expectations.

TYPES OF AUDITS
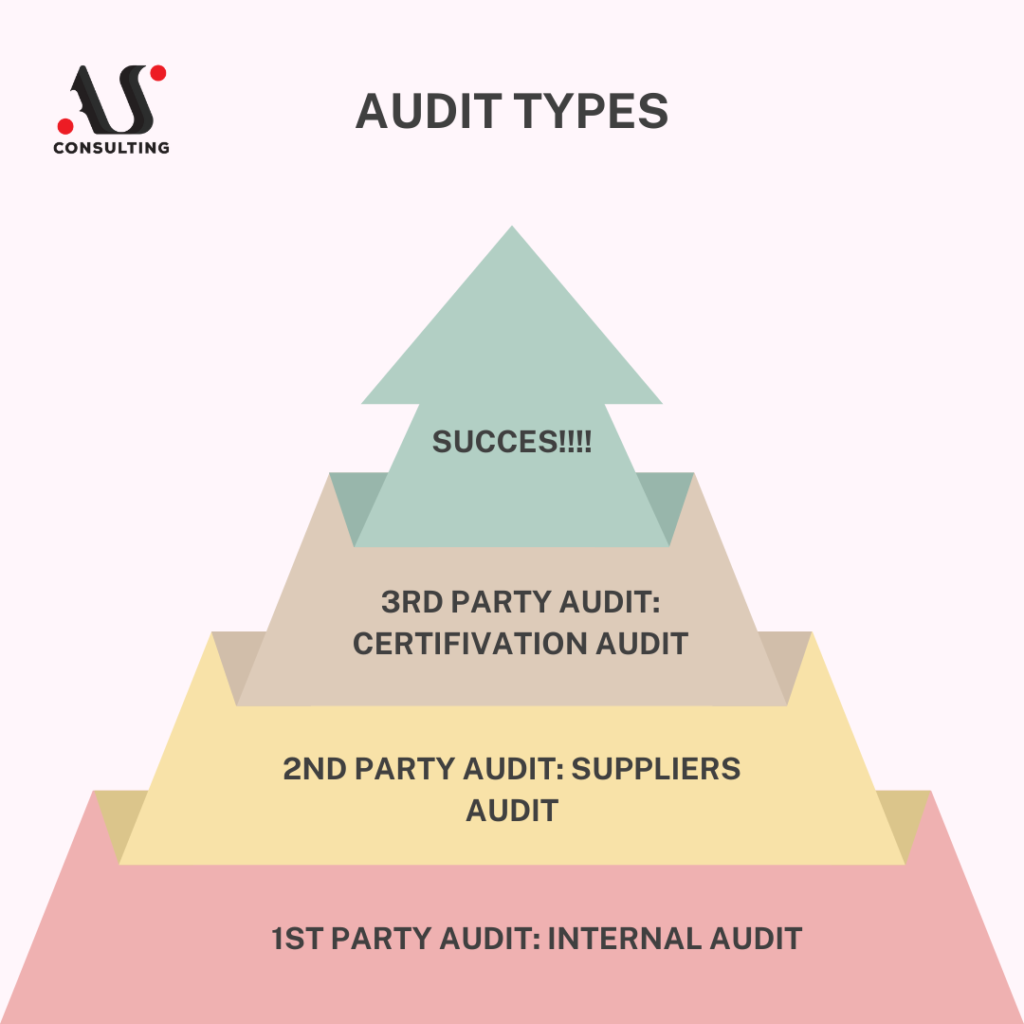
Methods for demonstrating conformity include testing, inspection, supplier’s declaration of conformity, and certification. Conformity assessment can be performed by product or service suppliers, customers, and other interested parties, resulting in different types of conformity assessments:
- First-party (the party providing the product and responsible for its conformity to specified requirements: first-party specifications, customer requirements, legal requirements)
- Second-party (a party interested in the subject matter that defines its requirements and is responsible for ensuring product conformity to those requirements)
- Third-party (an independent party not related to the first or second party
Most retail chains and large companies establish their own codes of practice and define detailed conditions related to quality management systems and product safety, which they expect their suppliers to adhere to. These conditions also pertain to equipment, environment, and legal regulations that suppliers must comply with.
Audits are essentially confirmations that operations adhere to established criteria, legal regulations, and quality and safety standards for products.
Retail chains have particular responsibility regarding private label products, as these products are marketed under their name and must meet requirements for accuracy, legality of data, health safety, and product correctness. Therefore, audits serve as a means for retail chains to ensure manufacturers operate according to the rules and standards they have set, as well as a guide for potential quality improvements and innovations. There are two types of audits:
- Planned audits – conducted when accepting a new supplier or as regular checks at planned intervals for existing suppliers (to obtain evidence of compliance with quality and safety criteria set by the retail chain).
- Unplanned audits – in cases of serious issues with deliveries, variable product quality, customer complaints, microbiological product defects, negative media reports, anonymous tips, product recalls and withdrawals.
If both parties, supplier and retail chain, approach an audit to improve the current situation, then the audit will be an opportunity to identify all advantages and disadvantages and enhance cooperation in mutual interest.
ANNOUNCED AND UNANNOUNCED AUDITS
Certification audits related to ISO standards, for example, are announced, meaning the certification body and the audited company agree in advance on the date and time of the audit.
Audits related to food safety standards (GFSI standards: IFS, BRC, FSSC22000, etc.) typically require an unannounced audit once every three years, meaning the audited company is not informed of the date and time of the audit. Even in this case, there is a timeframe when an unannounced audit can be conducted to comply with the “audit window” defined by each standard. Therefore, the audited company knows in advance the period during which an unannounced audit will be conducted.

But what about customer audits?
- Customer audits can also be announced or unannounced.
What does this depend on?
- It depends on the customer’s own procedures related to supplier control, risk analysis related to suppliers, customer audit policies, etc.
When can an announced customer audit be conducted?
- Similar to certification audits, at a mutually agreed time between the customer and the audited company.
When can an unannounced customer audit be conducted?
At any time; there is no connection here between the “audit window” and the timing of the audit itself. Based on their supplier verification plans, the customer can conduct the audit within a suitable timeframe.
What motivates unannounced customer audits?
Motives can vary:
- Principle that audits of all suppliers should be conducted without prior notice
- Any type of issue related to product quality and/or safety
- Suspicions of irregular implementation of requirements by the supplier
- Frequent complaints
Customer audits are often the gateway to working with a given customer. Therefore, thorough preparation is essential. For all consultation types, contact our Agency!!!!




