
CONTEXT OF THE ORGANISATION
September 17, 2020INTERNAL AUDIT(ON THE EXAMPLE OF IFS FOOD STANDARD)
February 2, 2021HACCP is a system (not standard!) whose name is abbreviation of the word: hazard analysis and critical control point.
According to the definition of the Codex Alimentarius, HACCP is: "a system which identifies, assesses and controls hazards that are important for the safety of food."
And what is Codex Alimentarius? - a set of internationally recognized standards, rules of conduct, guidelines and other recommendations related to food, food production and food safety .
How did HACCP come about? The application of the HACCP system in the field of food production began in the "Pilsbury" company, in cooperation with the National Aeronautics and Space Research Service (NASA), the "Natick" laboratory of the US Army and the project group from the aerospace laboratory of the USA.
The application of this system in the early 1960s led to the production of food for the space program of the USA, for which there was 100% certainty that it was not contaminated with bacterial and viral pathogens and toxins, and that there was no chemical or a physical hazard that could lead to illness or injury to the astronaut
HACCP replaced the final product testing and was a preventive system for the production of correct food with universal application. HACCP as a new concept was first introduced to the public in 1971 at the state conference on food protection, now that “Pilsbury” has received approval from the FDA (food and drug administration) to organize a training for FDA staff on the HACCP system.
The spread of HACCP around the world followed when it was published by the Codex Alimentarius commission as an Annex to Alinorm 93/13.
Prerequisites for HACCP.
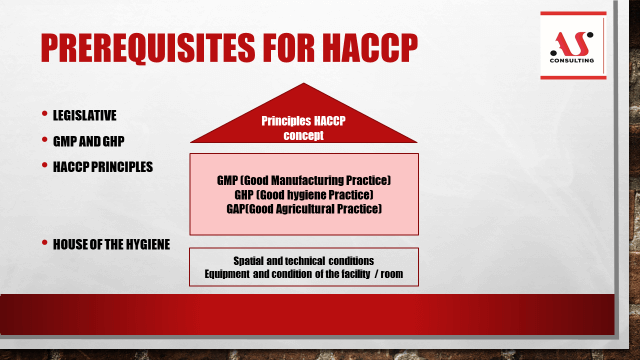
For the development of a good HACCP system, the establishment of previously required programs is of special importance. The programs to be adopted, implemented and documented are:
GMP (good manufacturing practice) - a set of procedures that manage working conditions and
GHP (good hygiene practice) - a set of procedures that manage the hygiene of the working environment and provide the basis for the production of safe food products
GAP (good agricultural practice) - a set of procedures that manage the conditions of primary production and provide the basis for the production of safe food products
HACCP plan framework and development.
a HACCP plan is a description of what that plan covers (scope)
the objective of the HACCP plan is to identify potential hazards, to assess where in the process they can lead to risks and where they can be controlled.
the HACCP plan is developed and applied for each product / product group when developing a HACCP plan, we go through: 12 HACCP steps / 7 HACCP principles

HACCP Steps:
Assemble HACCP team: HACCP team shall be multidisciplinary and team members shall have specific knowledge of HACCP, product(s) and process(es). Team shall appoint internal team leader and recieve training about HACCP principles. External experts may be include. Team shall have strong senior management support.
Describe product: There shall be full description of the product which includes: composition; physical, chemica, organoleptic, microbiological parameters; shelf life; storage conditions; legal requirements for the food safety of the product; packaging; transport conditions; allergen status; GMO status etc.
Identify intended use of the product: description of expected use of the product by end consumer; taking into account vulnerable consumer groups
Construct flow diagram: For each product (product group) construct a flow diagram which covers all process steps (including rework and reprocessing)
On-site confirmation of the flow diagram: On-site checks of the flow diagram by HACCP team
HACCP Principles:
(HACCP step 6) HACCP Principle 1: Conduct a hazard analysis for each step: For each step you have to determine physical, chemical, biological hazards. Then, for each identified hazard, at every process step, conduct a hazard analysis: consider the likely occurrence of hazards and severity of their adverse health effects.
(HACCP step 7) HACCP Principle 2: Determine critical control point (s): Use a tool (decision tree or other tool(s)) for each step and each identified hazard to determine a CCP – critical control point .
(HACCP step 8) HACCP Principle3:Establish critical limits for each CCP: According to definition: „critical limit is a maximum and/or minimum value to which a biological, chemical or physical parameter must be controlled at a CCP to prevent, eliminate or reduce to an acceptable level the occurrence of a food safety hazard”.For each CCP, the appropriate critical limits shall be defined and validated.
(HACCP step 9) HACCP Principle 4: Establish a monitoring system for each CCP: In order to ensure the movement of the CCP within the critical limits, it is necessary to establish monitoring procedures. What is being monitored? How is it monitored? Who monitor? Frequency? Where is the monitoring recorded? Who controls monitoring?
(HACCP step 10) HACCP Principle 5: Establish corrective actions: In the event that monitoring indicates that a particular CCP is not under control, adequate corrective actions shall be taken and documented. Such corrective actions shall also take into account any non-conforming products.
(HACCP step 11) HACCP Principle 6: Establish verification procedures: Verification procedures are established in order to confirm that the HACCP system is effective. Eg (internal audits, analysis, sampling, evaluations, compliant by authorities and customers).
(HACCP step 12) HACCP Principle 7:Establish documentation and record keeping: Documentation shall be available an cover all processes, procedures, control measures and records.

The implementation of a good HACCP system is the basis for upgrading food safety standards. If you need help with the proper establishment of the HACCP system, you can contact our agency. We successfully conduct online trainings, as well as on-site consulting.


